Hydrocephalus
Find your care
Our expert neurosurgery team is committed to providing the finest and most comprehensive patient care. For help finding a neurosurgeon, call 310-825-5111.
Hydrocephalus
General Information
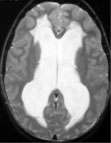
- Hydrocephalus is an abnormal accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) within cavities called ventricles inside the brain. CSF is produced in the ventricles, circulates through the ventricular system and is absorbed into the bloodstream. CSF is in constant circulation and has many important functions.
- It surrounds the brain and spinal cord and acts as a protective cushion against injury.
- The rapid movement of CSF within and around the brain may be important with regard to the flow of pulsatile blood through the brain.
- CSF may carry waste products away from surrounding tissues.
- Hydrocephalus occurs when there is an imbalance between the amount of CSF that is produced and the rate at which it is absorbed. As the CSF builds up, it causes the ventricles to enlarge and the pressure inside the head to increase.
- The causes of hydrocephalus are not well understood.
- Hydrocephalus that is congenital (present at birth) is thought to be caused by a complex interaction of environmental and perhaps genetic factors. Aqueductal stenosis and spina bifida are two examples.
- Acquired hydrocephalus may result from intraventricular hemorrhage, meningitis, head trauma, tumors and cysts.
- Hydrocephalus is believed to occur in about two out of 1,000 births. The incidences of adult-onset hydrocephalus and acquired hydrocephalus are not known.
Diagnosis
- Hydrocephalus is a disorder, not a disease, and therefore it is important to investigate the cause of hydrocephalus.
- The diagnosis of hydrocephalus is best confirmed by magnetic response imaging (MRI) of the brain. A computed tomography (CT) scan of the brain can also diagnose hydrocephalus. (But in most cases, an MRI is required afterwards.)
- In infants, ultrasound can also be used for initial diagnosis.
- The diagnosis of aqueductal stenosis, or other process causing an obstruction of ventricular CSF flow, can open possibilities for endoscopic treatment. When appropriate, an effort is made to investigate for meningitis or brain tumor.
Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of hydrocephalus vary with age and severity.- Infants
- Large or enlarging head
- Poor feeding
- Vomiting
- Sleepiness
- Irritability
- Downward deviation of the eyes (also called "sunsetting")
- Seizures
- Children and adults
- Headache followed by vomiting
- Nausea
- Papilledema (swelling of the optic disk which is part of the optic nerve)
- Blurred vision
- Diplopia (double vision)
- Sunsetting of the eyes, problems with balance
- Poor coordination
- Drowsiness
- Elderly (Normal pressure hydrocephalus)
- Progressive mental impairment and dementia
- Problems with walking
- Impaired bladder control leading to urinary frequency and/or incontinence
Treatment
- There is no known way to prevent or cure hydrocephalus.
- The most effective treatment is surgical insertion of a shunt.
- Endoscopic third ventriculostoy (ETV) is growing in popularity as an alternative treatment method for hydrocephalus.
The Neuro-ICU cares for patients with all types of neurosurgical and neurological injuries, including stroke, brain hemorrhage, trauma and tumors. We work in close cooperation with your surgeon or medical doctor with whom you have had initial contact. Together with the surgeon or medical doctor, the Neuro-ICU attending physician and team members direct your family member's care while in the ICU. The Neuro-ICU team consists of the bedside nurses, nurse practitioners, physicians in specialty training (Fellows) and attending physicians. UCLA Neuro ICU Family Guide