Embolization
Find your care
Our interventional neuroradiology team has paved the way for interventional procedures, creating several of the devices and techniques widely used today. Call 310-267-8761 to learn more about our services.
Embolization at UCLA
What is Embolization?
Embolization is a non-surgical, minimally invasive means of blocking the arteries that supply blood to diseased tissue such as tumors or malformations. Embolization procedure uses a microcatheter (very small plastic tube), which is navigated into the target arteries under X ray guidance. Small particles, glue, or coils are injected from the microcatheter so that the target arteries are blocked.
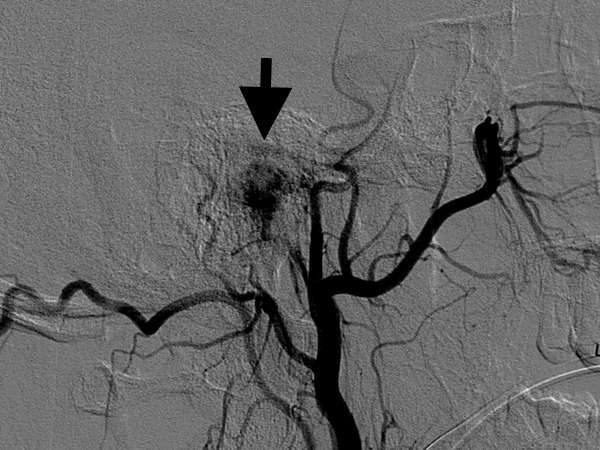
Figure 1: A black arrow indicates a shadow of tumor (Glomus tympanicum tumor). The more blood flow the tumor is supplied, the darker the shadow becomes.
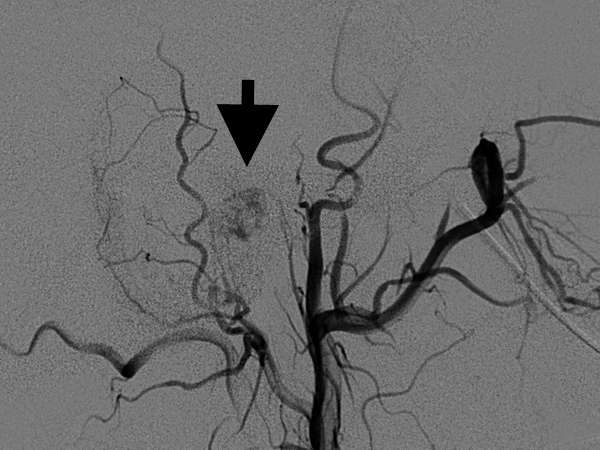
Figure 2: After embolization of small arteries that feed the tumor, the shadow becomes less dense, which indicates the tumor now receives less blood supply.
Embolization is also a very effective method to control or prevent bleeding. Brain aneurysm, arteriovenous malformations and dural arteriovenous fistula can be treated by embolization.