Breast Reconstruction
Find your care
UCLA Health’s Breast care specialists develop a personalized plan to help you recover. For more information, reach a cancer care specialist at 310-825-2144.
Breast Reconstruction after Surgery for Cancer
Overview
Breast reconstruction includes different surgical procedures performed by a plastic surgeon that can restore the natural size and shape of your breast after cancer surgery. Reconstructive surgery is an option for most woman who do not have strong medical or treatment-related contraindications and can be an important part of the healing process. In the United States, breast reconstruction is covered by insurance to restore a breast after cancer treatment. In many instances, insurance companies also cover reconstruction of the opposite breast to achieve symmetry.
If your cancer doctor feels you are a candidate for breast reconstruction, a plastic surgeon specializing in breast reconstruction will be a part of your surgical team and will perform the reconstructive portion of your surgery. Your breast cancer surgeon and plastic surgeon work very closely to not only consider appropriate treatment of your cancer but also plan for a preferred cosmetic result. Most-commonly, the first stage of the reconstruction is performed at the same time as your mastectomy (i.e. immediate breast reconstruction).
The two major techniques that can be used to reconstruct a breast include implant-based reconstruction or tissue-based reconstruction. The procedure that is best for you will depend on many factors including age, anatomy, medical history, or prior history of breast procedures. You and your reconstructive breast surgeon will decide which kind of reconstruction is right for you.
Types of Breast Reconstruction
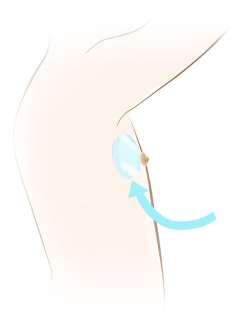
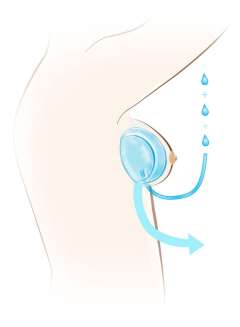
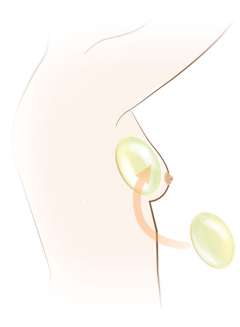
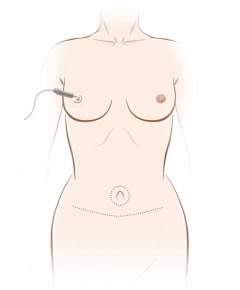
Implant-based reconstruction: Implant-based reconstruction is usually done in two stages. The first stage involves use of a “tissue expander”, which is a prosthetic balloon that is placed at the time of mastectomy. The expander is slowly filled with saline over the next weeks to months in the outpatient setting until the desired breast shape/size is achieved. After this, the expander is removed and a permanent implant is placed as part of an outpatient surgery. The time to complete this process can range significantly depending on preferred expansion rate, desired breast size, or other treatment-related factors. The average time is 3-6 months.
Variations in implant-based reconstruction exist in terms of positioning of the implant over or under the pectoralis muscle, and omission of the expander process and proceeding direct to implant. Several factors weigh into this decision-making process and should be discussed thoroughly with your reconstructive surgeon to determine what is the best approach for you. Typically, patients will stay one night in the hospital following a mastectomy and expander/implant placement and will have surgical drains in place that are removed 7-14 days after surgery.
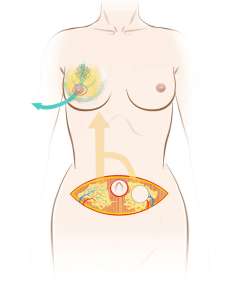
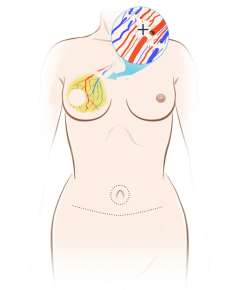
Tissue-based reconstruction: This type of reconstruction uses tissue from another part of your body to reconstruct the breast mound. The most common procedure is transferring fatty tissue from your abdomen to your chest. Tissue-based reconstruction requires a longer hospitalization and recovery than implant-based reconstruction, but patients tend to achieve a more natural look with this technique. At UCLA, our plastic surgeons are experts in Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator (DIEP) flaps which is a highly specialized microsurgical technique that allows them to reconstruct the breast with fat/skin from the abdomen without using the abdominal muscle. This creates a highly desired cosmetic result with less weakness to the abdominal wall compared to the conventional transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous (TRAM) technique which is more commonly performed at other centers.
Which reconstructive option is best for you will be based on several individual factors that will need to be discussed with your reconstructive surgeon.