Liver Cancer Chemoembolization
Find your care
Our experts offer a comprehensive suite of image-guided techniques to treat cancers of the liver, kidney, lung, musculoskeletal and other solid malignancies. Call 310-481-7545 to schedule a consultation or procedure.
Treatment for:
Why it’s done:
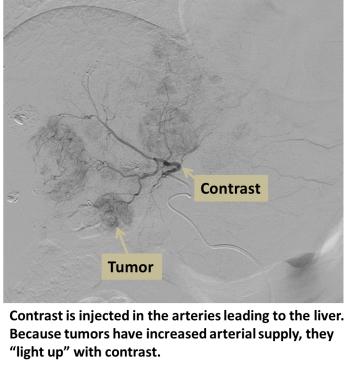
Normal liver tissue is supplied both by the hepatic artery and by the portal vein. Liver cancers, however, are supplied almost entirely by the hepatic artery. Treatment with chemotherapy in the hepatic artery (chemo), as well as blocking the hepatic artery branches supplying the tumor (embolization), can therefore help shrink and control liver cancers while sparing much of the normal liver.
How it’s done:
An interventional radiologist uses X-rays to guide a small catheter from the femoral artery at the groin and into the hepatic artery. Contrast injection is performed to locate the cancer(s) in the liver. Each artery branch supplying the cancer is then accessed using a microcatheter and chemotherapy as well as an embolic material is administered to kill the tumor and block its blood supply.
Level of anesthesia:
Conscious sedation
Risks:
Small risk of bleeding and infection. Risk of liver failure, which depends on the baseline liver function and the amount of liver treated. Small risk of non-target embolization, in which the embolic material blocks blood supply to an organ other than liver (such as the gallbladder, intestines, or stomach). Chemotherapy effects, which can include fatigue, low blood counts, and hair loss. Contrast dye and X-rays are used.
Post-procedure:
Generally, the procedure is followed by overnight admission. You will lie flat for several hours after the procedure. Post-embolization syndrome, which can include fatigue, abdominal pain, nausea, low-grade fever, and loss of appetite, can occur and typically lasts 24-48 hours. Most patients are discharged home the day after the procedure.
Follow-up:
A follow-up CT or MRI is usually performed 1 month after treatment along with clinic visit in interventional radiology to determine the results and allow for further treatment planning. Repeat chemoembolization may be performed as soon as 6 weeks after, if necessary. Sometimes chemoembolization can be followed by percutaneous ablation to attempt complete destruction of the cancer.
For More Information:
For more information or to schedule an appointment with one of our IR physicians, please call 310-481-7545.