Patient Education
Find your care
Our specialists offer comprehensive arrythmia care. To learn more about our services, call 310-206-2235.
Glossary
View video of Cardiac Arrhythmias
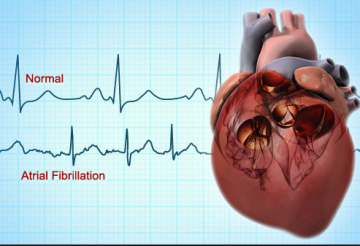
Arrhythmia:
An arrhythmia is an abnormal heart rhythm.
Some arrhythmias can cause problems with contractions of the heart chambers by:
-
Not allowing the ventricles (lower chambers) to fill with an adequate amount of blood because an abnormal electrical signal is causing the heart to pump too fast or too slow.
-
Not allowing a sufficient amount of blood to be pumped out to the body because an abnormal electrical signal is causing the heart to pump too slowly or too irregularly.
-
Not allowing the top chambers to work properly.
In any of these situations, the body's vital organs may not receive enough blood to meet their needs.
Atria: The two upper chambers of the heart - one on the right, one on the left.
Bradycardia: A heart rate of less than 60 beats per minute is called bradycardia. The average resting heart rate is 60 to 100 beats per minute.
Palpitations: A symptom sometimes associated with arrhythmias. It is often described by people as a sensation of the heart "skipping," "jumping," "fluttering" or "racing."
Tachycardia: A fast heart rate, usually greater than 100 beats per minute.
Ventricles: The two lower chambers of the heart - one on the right, one on the left.
Helpful Links
Visit our Resources and Links page for helpful links regarding heart rhythm problems and various cardiac procedures.