External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT)
3D conformal therapy
This is a radiation technique where multiple radiation beams are used to conform to a target. The dose of radiation that is delivered from each radiation field is shaped by small leaves in the head of the radiation treatment machine called multileaf collimators. The intensity of the radiation from each field is uniform which is different than with intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT). Below is an example of what the treatment fields look like on an X-ray when treating the pelvis.
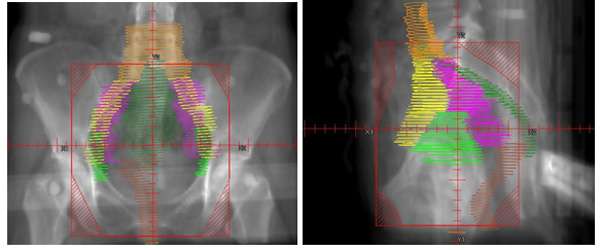
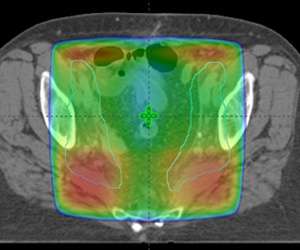
One can see that the radiation dose covers the entire pelvic region but the actual target on this slice, which can be seen in the pale blue outlines on the right and left sides of the pelvis, is actually much smaller. Ideally we would be able to sculpt the radiation to these pale blue regions and to spare the middle part of the pelvis from unnecessary radiation. Advances in radiation with intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) give us the ability to accomplish this.
- Request an appointment
- Westwood: 310-825-9775
- Santa Monica: 424-259-8777