Facet Joint Arthritis
Find your care
At the UCLA Health Spine Center, our experts diagnose, manage and treat all spinal injuries and conditions. Call 310-319-3475 to connect with a spine specialist.
Fax: 424-259-6560
What You Should Know About Facet Joint Arthritis
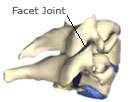
The spine is formed by the bones (vertebral bodies), which are stacked one on top of another. On each side of the vertebral bodies, are tiny joints called facet joints. Arthritic changes and inflammation can develop in these joints, and the nerves to the facet joints can convey severe and diffuse pain.
Symptoms
The pain does not follow a nerve root pattern. It is actually called "referred pain," as the brain has trouble localizing these internal structures. Patients often complain of pain in a generalized, poorly defined region of the neck or back. Pain is usually worsened by sudden movements or prolonged episodes of poor posture, (e.g., kneeling in the garden, bending over to lift, or straining to read a book or look at a computer terminal). Many patients find the worst time is at night, when all the muscles relax and the arthritic joints grind together.
![X-ray [CT scan] showing the facet joint in cross-section](/sites/default/files/styles/max_width_004000_160/public/images/Facet_Jsynd.02.jpg?f=501a759b&itok=IE6yXl6r)
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of facet joint arthritis is made by physical examination, X-ray, or MRI. A diagnostic block (injection) into the facet joint or nerves that supply the joints can often confirm the facet joints as the source of pain.
Treatment

A heating injection procedure called radiofrequency ablation can be used to treat facet joint arthritis. Its goal is to block the nerves that send pain from the facet joints.