Neural Tube Defect Screening
Find your care
Maternal fetal specialists provide advanced care and support to you and your baby. Call 310-794-7274 to connect with our high-risk pregnancy experts.
What are open neural tube defects (ONTDs)?
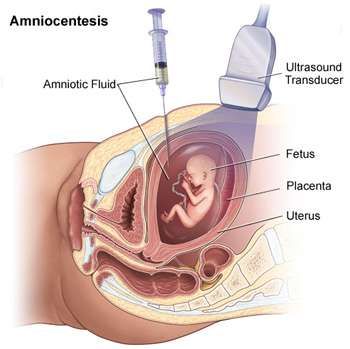
Open neural tube defects (ONTDs) are defects in the primitive spine, called the neural tube, such as spina bifida (open spine) and anencephaly (open skull).
Maternal and Fetal Testing
To evaluate the health of a pregnancy and fetus, many types of prenatal tests may be performed.
The vast majority of women have healthy pregnancies and their babies are born without difficulties. However, women with high-risk pregnancies often need a close watch for potential problems or complications. Fortunately, there are many tests and procedures to monitor the health of both mother and baby. Many of these pose little or no risk and can provide tremendous amounts of information to doctors, midwives, and expectant parents. Some types of testing and procedures, however, do carry some risks to mother, baby, or both. For this reason, if you are offered prenatal testing, it is important to discuss with your doctor or midwife the following questions:
- Why is the test needed for your pregnancy?
- What information will the test provide?
- What are the benefits of the test?
- What are the risks, if any, to you and to your baby?
- What other tests might be used instead?
- Who will perform the test?
- Where will it be done?
- How long does it take to get results?
- Will the test results require additional testing?
- What are your options based on the outcome of the test?
- What are your options if you choose to not have the test?
Some mothers are more likely to need a closer watch on their pregnancy. Some conditions that may warrant maternal and fetal testing include the following:
- Pre-existing maternal diseases (for example, diabetes, kidney disease, heart disease)
- High blood pressure
- Abnormal amniotic fluid amounts
- Abnormal fetal growth
- Multiple pregnancy (twins or more)
- Post-term pregnancy