Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
Find your care
Our clinic is nationally and internationally renowned for IVC filter removal. Call 310-481-7545 to learn more about the IVC Filter Clinic at UCLA Health.
What is a pulmonary embolism (PE)?
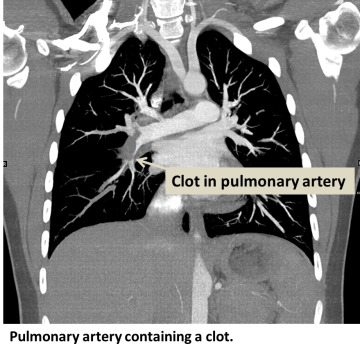
A pulmonary embolism (PE) occurs when an artery in the lungs becomes blocked. The blockage is usually caused by a blood clot that travels to the lungs from the legs, which is a result of deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
The pulmonary embolus blocks blood flow to part or all of the lung, and can often be life-threatening. Occlusion of blood vessels of the lungs can lead to increased blood pressure in the lungs called pulmonary hypertension, and can result in heart failure. Pulmonary emboli can also decrease the amount of oxygen in the blood.
Risk Factors
- Deep vein thrombosis
- Inactivity
- Obesity
- High blood pressure
- Smoking
- Major surgery
- Some cancers and chemotherapy
- Heart attack
- Stroke
- Pregnancy
- Birth control pills
- Hormone replacement therapy
- Disorders with increased clotting, such as the Factor V Leiden mutation
Symptoms
Pulmonary emboli can be life-threatening and should be treated immediately. If untreated, PE can be deadly.
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
- Lightheadedness
- Chest pain, especially when coughing or exercising
- Coughing blood
- Blue lips or fingers (cyanosis)
- Increased heart rate
Diagnosis
A physical exam showing the above symptoms may help your healthcare provider diagnose PE, especially you have deep vein thrombosis, but the following tests may also be used:
- D-dimer blood test
- Computed tomographic angiography (CTA)
- Pulmonary angiography using X-rays and a catheter inserted into the pulmonary arteries
- Nuclear Medicine lung scan to measure air and blood flow in lungs
Other tests may also be performed to test for related conditions or complications. Some of these tests include but are not limited to:
- Doppler ultrasound of the legs
- Electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG)
- Echocardiogram, an ultrasound of the heart