Adolescent Bariatric Surgery
Find your care
Our bariatric surgeons use a range of treatments to help you reach weight loss goals and optimize your health. To learn more, call 310-206-0367.
With the obesity epidemic, childhood obesity has become one of the most important public health problems in the United States. The national childhood obesity rate has reached 18.5% in 2015-2016.
Children and adolescents affected by obesity are at an increased risk of developing obesity related comorbidities such as diabetes, hypertension, obstructive sleep apnea, fatty liver disease, slipped capital femoral epiphysis, polycystic ovarian syndrome.

Adolescents with severe obesity are also at higher risks of having low self-esteem, depression, anxiety, discrimination, and impaired social relationship. Diet and exercise are the recommended initial treatment for adolescents with obesity. However, if the degree of obesity is severe, dietary and behavioral interventions alone generally fail in the long-term.
Based on large amount of data from adults and recent data from adolescent bariatric surgery, the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS) recommended that bariatric surgery should be considered for adolescents with: (1) BMI greater than 35 kg/m2 or 120% of the 95th percentile with a co-morbidity, or (2) BMI >40 kg/m2 or 140% of the 95th percentile without a co-morbidity (whichever is less).
The benefits of bariatric surgery in adolescents include:
Reduction of cardiovascular disease risks
The Teen-LABS research consortium study showed high prevalence of cardiovascular-related risk before bariatric surgery and significant improvement in the overall prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors after surgery. Bariatric surgery significantly improved hyperlipidemia, inflammation, hypertension, and insulin resistance and decreased morbidity and mortality from cardiovascular disease in the long term.
Improvement/remission of Type 2 diabetes
Children with obesity face four times the risk of developing type 2 diabetes compared to children with normal weight. Having diabetes at young age significantly increases the long-term health risks. When children develop type 2 diabetes at age 10, many of them can expect a risk of co-morbidities by age 15. Early onset type 2 diabetes fails medical therapy in >50% of cases and has a poor outcome with respect to end organ damage and early mortality. Recent studies have demonstrated excellent results showing remission of prediabetes in 76% and type 2 diabetes in 95% of adolescents. Childhood-onset type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance should be considered strong indications for bariatric surgery.
Resolution of Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)
OSA in obese adolescents is estimated to be 4-5-folds higher than their peers with normal weight and up to one-third of children and adolescents with obesity may have OSA. Positive airway pressure is effective for treating OSA (using CPAP machine at nighttime); however, many adolescents do not like to use those machines. Bariatric surgery leads to significant improvement or resolution of OSA and many adolescents no longer need the CPAP machine after surgery.
Resolution of Fatty liver disease
Obese children and adolescents have higher risk of developing fatty liver disease, also called non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Simple fatty liver disease has fat accumulation in the liver, but no inflammation or cell damage. When simple fatty liver disease progresses, inflammation and cell damage can happen and this is called non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Recent studies have shown complete resolution of NASH in approximately 85% of patients who undergo bariatric surgery. NAFLD and NASH should be considered a strong indication for bariatric surgery in children and adolescents with severe obesity.
Improvement of Quality of life
Compared with normal weight peers, adolescents with severe obesity generally have severely impaired quality of life. Many obese adolescents experience weight related physical discomfort (fitting into public seating), low self-esteem (shame due to weight), impaired social life (teasing because of weight), depression and anxiety. With the weight loss from bariatric surgery, adolescents reported marked and sustained improvement of quality of life.
Type of weight loss surgery
Today, the most commonly performed weight loss surgery in adults and adolescents worldwide is sleeve gastrectomy. Compared with gastric bypass surgery, it has near-equivalent weight loss in adolescents, fewer reoperations, better iron absorption, and near-equivalent effect on co-morbidities resolution/improvement. However, we do not have long-term data available for sleeve gastrectomy yet. In this case, both gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy can be considered for adolescents.
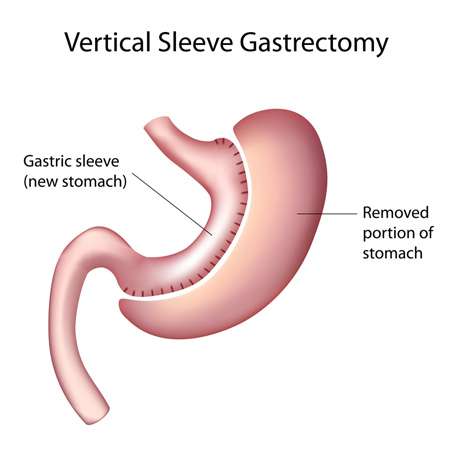
Gastric Sleeve Surgery
The Gastric Sleeve Surgery (or Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy) is a bariatric procedure that removes 75-80% of the stomach.
Gastric sleeve aids weight loss by:
- Gastric Sleeve Surgery brings profound changes to life!
- Overall improved quality of life
- Excess weight loss of about 60-70% within one year of surgery
- Remission or improvement of obesity related health conditions such as diabetes mellitus type II, hypertension, sleep apnea, fatty liver disease, joint pain, and hyperlipidemia
- Desire to eat decreases
- Reduction in hunger sensation
For more information about the Sleeve Gastrectomy, please visit: Sleeve Gastrectomy Information
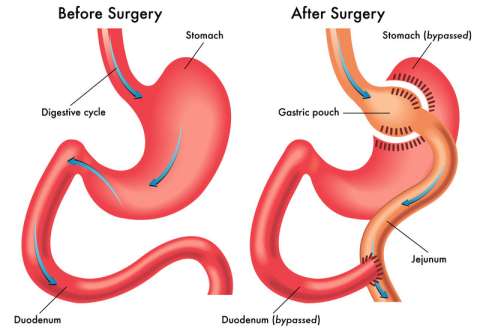
Gastric Bypass Surgery
Gastric bypass surgery is a type of bariatric, or weight loss surgery. During gastric bypass surgery, your physician makes changes to your stomach and small intestine to change the way they absorb and digest food.
Gastric bypass aids weight loss by:
- Restricting the amount of food that your stomach holds
- Limiting the amount of calories and nutrients your body absorbs
- Changing your gut hormones, which help you feel fuller longer, contribute to appetite suppression and the reversal of obesity-caused metabolic syndrome.
For more information about the Gastric Bypass, please visit: Gastric Bypass
Contact Us
To schedule a consultation with UCLA Bariatric Surgery in Los Angeles, California, call us at or fill out our .
For a physician referral, please call.
*Weight loss results can vary depending on the individual. There is no guarantee of specific results. Read full disclaimer.