Colloid Cyst
Find Your Care
Our expert neurosurgery team is committed to providing the finest and most comprehensive patient care. For help finding a neurosurgeon, call 310-825-5111.
About Colloid Cyst
A colloid cyst is a slow-growing tumor typically found near the center of the brain.
If large enough, a colloid cyst obstructs cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) movement, resulting in a build up of CSF in the ventricles of the brain (hydrocephalus) and elevated brain pressure.
Symptoms
- Most patients present with headaches, although other symptoms can occur.
- If symptomatic, prompt surgical treatment may be required in order to reduce the relatively high risk of sudden death.
Treatments
Minimally invasive surgery techniques
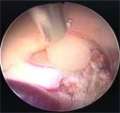
Minimally invasive techniques are used by UCLA neurosurgeons for the removal of colloid cysts. For patients with hydrocephalus, several options are available at UCLA:
- Endoscopic removal - endoscopy typically requires very small bony opens.
UCLA neuroendoscopic surgeons have expertise with both single and dual-port approaches - 11.5-mm sleeve transcortical microsurgical removal
The 11.5 mm diameter surgical port allows the use of a wider range of microsurgical instruments compared to the neuroendoscope.
State-of-the-art image fusion and neuronavigation technology allow UCLA neurosurgeons to select the optimal pathway that minimizes brain tissue injury.
The scalp incision size is similar to endoscopic technique - Microcraniotomy interhemispheric microsurgical removal
For patients with symptomatic or large colloid cysts but without significant hydrocephalus.
Using state-of-the-art image fusion and neuronavigation technology, UCLA neurosurgeons can remove colloid cysts without the need to injure cortical brain tissue.
UCLA neurosurgeons have expertise in surgical techniques that do not require the use of damaging brain retractors.
The scalp incision size is only slightly longer than endoscopic and sleeve techniques - More about minimally invasive surgery
CSF shunt
- Placement of a shunt to drain CSF may be recommended if removal of the cyst is considered too high risk or if hydrocephalus continues despite removal of the cyst.
The Neuro-ICU
The Neuro-ICU cares for patients with all types of neurosurgical and neurological injuries, including stroke, brain hemorrhage, trauma and tumors. We work in close cooperation with your surgeon or medical doctor with whom you have had initial contact. Together with the surgeon or medical doctor, the Neuro-ICU attending physician and team members direct your family member's care while in the ICU. The Neuro-ICU team consists of the bedside nurses, nurse practitioners, physicians in specialty training (Fellows) and attending physicians.